White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) risk factors associated with managerial shrimp farming practices through expert opinion in monoculture farms in Iran
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17762/sfs.v9i1.19Keywords:
Cultured shrimp, WSSD, Managerial factors, Gowmishan, GolestanAbstract
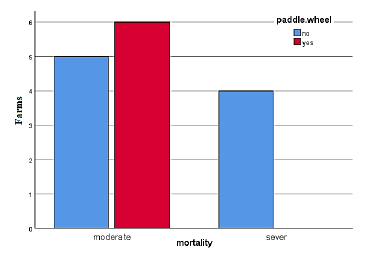
The objective of this study was to investigate the relationship of managerial factors with incidence WSSV severity in shrimp farms located in Golestan province of Iran. This research was carried out in cooperation with Iran Fisheries Org- Office of Shrimp, General directorate of Golestan Province, in cooperation with the Fisheries Science Research Institute and the Stock Assessment of Inland Water Research Center, on the shrimp farms of Gomishan site in Golestan, in 2019. The data were designed using a questionnaire addressing thirteen variables such as educational level, temperature fluctuation, Mortality in shrimp farms, removing the pond bottom sludge, stocking density of PLs and pre-stocking test. According to the opinion of shrimp farmers, Pearson’s Chi-square showed a significant relation between severity of mortality and weather temperature (p=0.049). effect of types of monthly salary on the severity of WSSV occurrence has been significant. shrimp PLs stocking in ponds showed a significant effect on the severity of white spot disease WSD. It is concluded that a few managerial factors such as PLs origination, lowering the temperature, pre-stocking test and stocking density are critical indicators, which can effect on severity of mortality in WSSV outbreak.