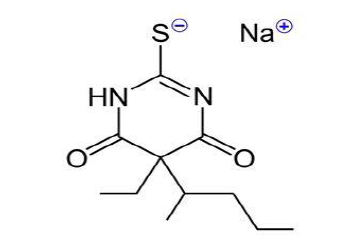
Anaesthetic effect of Sodium-Thiopental by bath on the three different body weights of Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum, 1792)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17762/sfs.v8i3.41Keywords:
Fish, Rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, Sodium -thiopental, Anesthesia, Aquaculture, PharmacologyAbstract
The aim of this study was the efficacy of sodium-thiopental as an aneasthetic by bath on three different body weights of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). During the experiment, aeration had done and physicochemical properties of water such as dissolved O2, temperature and pH were recorded. Trouts were sorted into three groups with different mean body weights of 8.31±0.36g, 22.58±0.61g and 81.61±1.76g. Every three groups were anaesthetized by bath, with 100 mg/L (100 ppm) of sodium-thiopental concentration. The results showed that the induction and recovery times, being significantly affected by sodium-thiopental, so that, these were shorter in the heavier fish. Anaesthesia duration for the fish with different mean body weights of 8.31±0.36g, 22.58±0.61g and 81.61±1.76g were thiopental with the weight of fish. So that the elapsed and recovery times were shorter in more weight fish than lighter ones.271±64.88, 240±3.33 and 231±76.47 seconds respectively. Also, recovery times were 448±67.81, 415±10.80 and 383±57.55 seconds respectively. Monitoring for 2 hours was shown that all fish have been alive. So, 100mg/L concentration of sodium thiopental is safe in the trout. The results of the present study showed that there was an inverse relationship between the elapsed and recovery times of sodium.