The effect of the current treatment protocol on some biochemical and inflammatory markers in severe COVID-19 patients
Main Article Content
Abstract
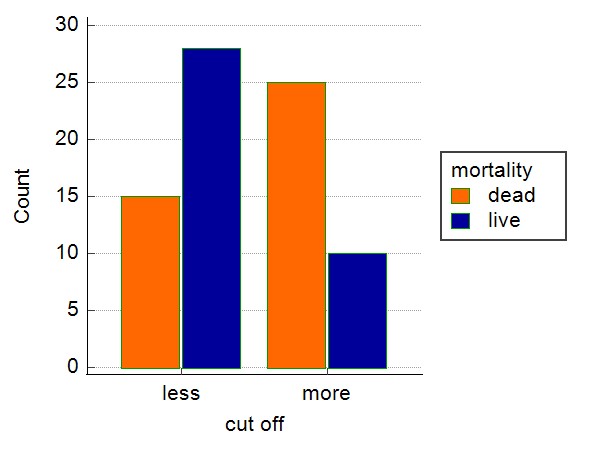
Treatment of coronavirus infections varied according to the severity of the symptoms, sites, and organs affected. COVID-19 severity ranged from mild, moderate, severe, and critical which may end in death. Disease treatment varied according to the stage, symptoms, and organs affected. Anti-virals, anti-inflammations, anti-bacterial, and anti-coagulants are commonly used in the treatment in addition to the tools helpful in improving respiration. To assess the efficacy of the current protocol used for the treatment of severe COVID-19 patients, forty severe COVID-19 cases admitted to al-Kindy hospital, Baghdad during the period from March 2021 to October 2021 were subjected to some biochemical and immunological tests thought to associate with the response to the therapy, disease progression, and mortality. After ten days of treatment, twenty patients died. When compared to the survivors, dead patients were of higher ages, had higher levels of urea, creatinine, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and D-dimer.
The correlation test revealed a significant positive correlation between mortality and IL-6 and D-dimer increase. Among all parameters tested in the study, ROC curve analysis showed that D-dimer has the largest area under the curve followed by IL-6 concerning mortality which indicated that these parameters are good predictors for disease progression and mortality outcome.