Effect of the PH on the Stability Constants of a Number of Azo Dyes Formed from the Reaction of (Diazotized 4-Aminobenzophenone) with a Some of Schiff Bases
Main Article Content
Abstract
In this research, we dealt with a spectroscopic study about the effect of the acidity function on the formation
thermodynamics of azo-dyes prepared from the reaction of the diazotized reagent (4-aminobenzophenone) with six
aromatic Schiff bases at three different acidic media, at a constant temperature (298K). We first determined the optimal
conditions for each prepared azo-dye and the optimal mole-ratios for its components, which were (1:1) for (Schiff's base:
reagent).
Then we found the degree of association of the colored azo-dyes formed, from which we calculated the stability constants
for their formed dyes at the three pH and at the five temperatures (273, 283, 293, 303 and 313 K). Then we studied and
determined the following factors affecting the stability-constant values of the formed dye:
A- Effect of pH: At three different acidic media and at the five different temperatures mentioned: We calculated the
stability constants of all six prepared dyes, and we obtained different values of stability constants, and these values are
considered evidence of the preparation of the six stable azo-dyes.
B- The effect of temperature: We found the stability constant values of the formation of all six prepared dyes at the five
temperatures, which allowed us to know that the reactions for the formation of azo-dyes are spontaneous and exothermic,
from the negative values of 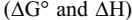 respectively, as well as the negative value For
respectively, as well as the negative value For 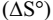 for most of the dyes
for most of the dyes
supports the aforementioned.
